Do People With Adhd Have More Intense Dreams
Dreams of people with ADHD are known to be vivid compared to neurotypical peers. Studies have shown that such vivid dreams and frequent nightmares may be a result of the brain's reward system being overactive in people with ADHD.
The study of dreams in people with ADHD has provided valuable insights into the disorder. It has helped researchers understand the neural mechanisms underlying ADHD and its impact on cognitive and emotional processes. Furthermore, it has led to the development of targeted interventions to improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares in people with ADHD.
This article will explore the relationship between ADHD and intense dreams, discussing the causes, consequences, and potential treatment options for this phenomenon.
Do People With Adhd Have More Intense Dreams?
Understanding the relationship between ADHD and intense dreams requires examining various key aspects. These include:
- Neurobiology
- Sleep patterns
- Dream content
- Emotional regulation
- Cognitive processes
- Treatment implications
- Comorbidities
- Long-term outcomes
These aspects provide a comprehensive framework for exploring the complex interplay between ADHD and intense dreams. By investigating the neurobiological underpinnings, sleep disturbances, and psychological factors involved, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of this phenomenon and develop effective interventions to improve sleep quality and overall well-being in individuals with ADHD.
Neurobiology
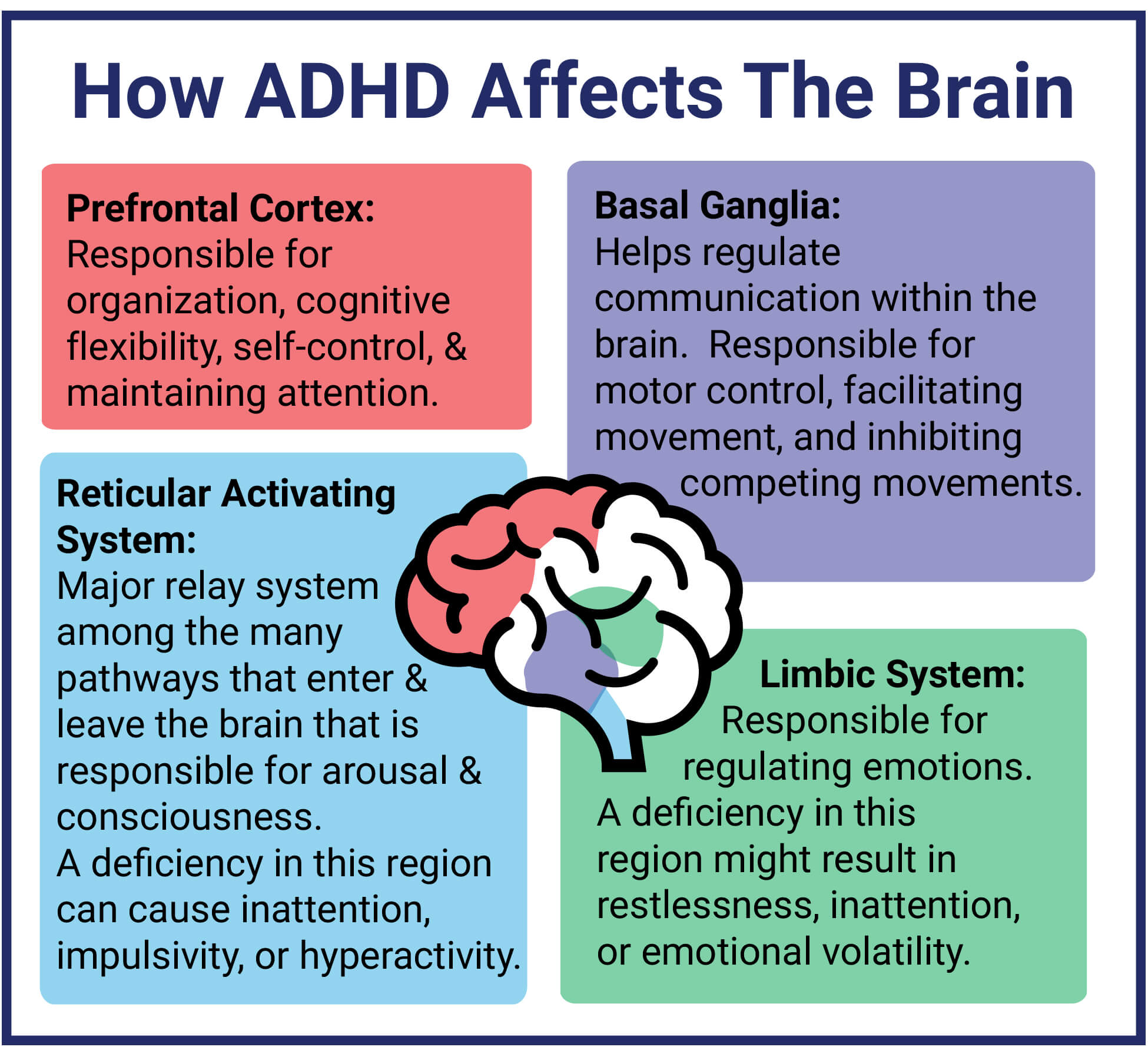
Neurobiology plays a crucial role in understanding the relationship between ADHD and intense dreams. It involves studying the structure and function of the brain and nervous system to elucidate the neural mechanisms underlying ADHD and its impact on sleep and dreaming.
- Brain Connectivity
Individuals with ADHD exhibit atypical brain connectivity patterns, particularly in regions involved in attention, emotion, and executive functioning. This altered connectivity may contribute to the vivid and intense dreams experienced by people with ADHD. - Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, are involved in regulating attention, arousal, and sleep-wake cycles. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters, commonly observed in ADHD, may disrupt sleep and lead to more intense dreams. - Frontal Lobe Function
The frontal lobe is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions, including attention, planning, and impulse control. Deficits in frontal lobe function, as seen in ADHD, may impair the ability to regulate emotions and suppress vivid dream content. - Sleep Architecture
People with ADHD often experience disrupted sleep architecture, characterized by reduced deep sleep and increased REM sleep. These sleep disturbances may contribute to the increased intensity and frequency of dreams.
These neurobiological factors provide a foundation for understanding the complex interplay between ADHD and intense dreams. Further research in this area can lead to the development of targeted interventions to improve sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares in people with ADHD.
Sleep patterns
Sleep patterns are intricately connected to the occurrence of intense dreams in individuals with ADHD. Atypical sleep patterns, including reduced deep sleep and increased REM sleep, are commonly observed in people with ADHD.
The disruption of deep sleep, which is essential for restorative and rejuvenating processes, may lead to increased dream intensity. Furthermore, the increase in REM sleep, the stage of sleep associated with dreaming, provides more opportunities for vivid and intense dreams to occur.
Real-life examples illustrate the relationship between sleep patterns and intense dreams in ADHD. Individuals with ADHD often report experiencing difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and waking up feeling unrefreshed. These sleep disturbances can contribute to the increased frequency and intensity of their dreams.
Understanding the connection between sleep patterns and intense dreams in ADHD has practical applications. By addressing sleep disturbances and promoting regular sleep-wake cycles, clinicians can help improve sleep quality and reduce the occurrence of intense dreams in individuals with ADHD. This can lead to improved overall well-being, cognitive functioning, and emotional regulation.
Dream content
Dream content, referring to the specific events, emotions, and imagery experienced in dreams, plays a crucial role in understanding their relationship to ADHD. Individuals with ADHD often report having more intense and vivid dreams, with unique characteristics that set them apart from the dreams of neurotypical individuals.
One key connection between dream content and ADHD is the heightened emotional intensity experienced in dreams. People with ADHD tend to have dreams that are more emotionally charged, with stronger feelings of joy, sadness, fear, or anger. This emotional intensity can contribute to the overall vividness and memorability of their dreams.
Moreover, the content of dreams in ADHD often reflects the individual's waking experiences and concerns. Studies have shown that people with ADHD are more likely to have dreams related to their daily challenges, such as academic or social difficulties. These dreams can provide insight into the individual's inner thoughts and feelings, helping clinicians better understand their unique experiences.
Understanding the connection between dream content and ADHD has practical applications in therapeutic settings. By analyzing dream content, clinicians can gain a deeper understanding of their clients' emotional states, identify potential triggers for intense dreams, and develop strategies to improve sleep quality and reduce dream-related distress.
Emotional regulation
Emotional regulation, the ability to manage and respond to emotions in a healthy and adaptive manner, plays a crucial role in understanding the relationship between ADHD and intense dreams. Deficits in emotional regulation are commonly observed in individuals with ADHD, and these difficulties can contribute to the vivid and emotionally charged dreams they experience.
One of the key connections between emotional regulation and intense dreams in ADHD is the heightened emotional reactivity experienced by individuals with this condition. People with ADHD often have difficulty controlling their emotions, which can lead to emotional outbursts, irritability, and impulsivity. This emotional dysregulation can carry over into their dreams, resulting in more intense and emotionally charged dream experiences.
Moreover, emotional regulation difficulties can impair the ability to suppress negative thoughts and feelings before bedtime. This can lead to an increase in dream anxiety and nightmares. Individuals with ADHD may also have difficulty calming themselves down before sleep, which can contribute to more vivid and intense dreams.
Understanding the connection between emotional regulation and intense dreams in ADHD has practical applications in therapeutic settings. By addressing emotional regulation difficulties, clinicians can help individuals with ADHD improve their sleep quality and reduce the frequency and intensity of their dreams. This can lead to improved overall well-being, cognitive functioning, and emotional stability.
Cognitive processes
Cognitive processes play a vital role in understanding the relationship between ADHD and intense dreams. They encompass the mental operations involved in acquiring knowledge, processing information, and making decisions.
- Attention and Focus
Individuals with ADHD often have difficulty sustaining attention and focusing on specific tasks. This can lead to fragmented and disorganized dream content, as their minds wander more easily during sleep.
- Working Memory
Working memory is responsible for temporarily storing and manipulating information. Difficulties with working memory in ADHD can impair the ability to consolidate dream experiences into coherent narratives, resulting in fragmented and surreal dreams.
- Executive Functioning
Executive functioning encompasses higher-order cognitive processes such as planning, decision-making, and impulse control. Deficits in executive functioning in ADHD can lead to difficulty regulating emotions and suppressing negative thoughts before bedtime, contributing to more intense and emotionally charged dreams.
- Metacognition
Metacognition refers to the ability to reflect on and understand one's own thoughts and feelings. Individuals with ADHD may have difficulty metacognitively evaluating the intensity and content of their dreams, which can hinder their ability to effectively manage dream-related distress.
These cognitive processes are intricately connected to the occurrence and characteristics of intense dreams in ADHD. By addressing cognitive difficulties and enhancing cognitive skills, clinicians can help individuals with ADHD improve their sleep quality and reduce the frequency and intensity of their dreams.
Treatment implications
Investigating the treatment implications of intense dreams in ADHD is crucial for developing effective interventions to improve sleep quality and overall well-being. These implications encompass various aspects, including pharmacological treatments, non-pharmacological interventions, and psychological approaches.
- Pharmacological Treatments
Medications commonly used for ADHD, such as stimulants and non-stimulants, can have an impact on dream intensity. Stimulants may reduce dream vividness, while non-stimulants may have varying effects depending on the individual.
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions
Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and habit reversal training, can help individuals with ADHD manage their sleep hygiene and develop strategies to reduce dream intensity.
- Psychological Approaches
Dream interpretation and dream journaling can provide insight into the underlying emotional and psychological factors contributing to intense dreams in ADHD, allowing for targeted interventions.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and establishing a consistent sleep-wake cycle can positively impact sleep quality and reduce dream intensity in individuals with ADHD.
Understanding the treatment implications of intense dreams in ADHD empowers clinicians with a range of options to address this common symptom. By tailoring interventions to the individual's needs and preferences, clinicians can effectively improve sleep quality, reduce dream-related distress, and enhance overall well-being in individuals with ADHD.
Comorbidities
Comorbidities, the presence of one or more additional mental health conditions alongside ADHD, play a significant role in understanding and treating intense dreams in individuals with ADHD. The relationship between comorbidities and intense dreams is multifaceted, involving both cause-and-effect dynamics and practical implications.
Certain comorbidities, such as anxiety disorders and mood disorders, can contribute to increased dream intensity in ADHD individuals. Anxiety and mood symptoms can lead to heightened emotional arousal and difficulty regulating emotions, which can carry over into dreams, making them more vivid and emotionally charged. Moreover, sleep disturbances associated with comorbidities, such as insomnia and nightmares, can further exacerbate dream intensity.
Real-life examples illustrate the impact of comorbidities on dream intensity in ADHD. Individuals with ADHD and co-occurring anxiety disorders may experience frequent nightmares related to their anxious thoughts and worries. Similarly, those with ADHD and depression may have dreams characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or low self-esteem.
Understanding the connection between comorbidities and intense dreams in ADHD has practical applications. Clinicians can assess for the presence of comorbidities and address them in treatment planning. By targeting both ADHD symptoms and comorbid conditions, clinicians can effectively reduce dream intensity and improve overall sleep quality in individuals with ADHD.
Long-term outcomes
Understanding the long-term outcomes associated with intense dreams in ADHD is crucial for developing comprehensive treatment plans and supporting individuals with this condition throughout their lives. Long-term outcomes refer to the lasting effects and consequences of ADHD and its symptoms, including intense dreams, over an extended period.
Long-term outcomes are intricately connected to the severity and persistence of ADHD symptoms, including the frequency and intensity of intense dreams. Individuals with persistent intense dreams may experience ongoing sleep disturbances, emotional difficulties, and cognitive impairments. These challenges can have a cumulative effect on daily functioning, academic performance, and overall well-being.
Real-life examples illustrate the impact of intense dreams on long-term outcomes in ADHD. Individuals who experience frequent nightmares and vivid dreams may develop sleep anxiety, avoidance of bedtime, and daytime fatigue. These sleep disturbances can lead to difficulties concentrating, irritability, and impaired social interactions.
Understanding the relationship between intense dreams and long-term outcomes in ADHD has practical applications. Clinicians can assess for the presence and severity of intense dreams as part of routine ADHD evaluations. By addressing intense dreams and associated sleep disturbances, clinicians can improve sleep quality, reduce emotional distress, and enhance overall functioning in individuals with ADHD.
In conclusion, the exploration of "Do People with ADHD Have More Intense Dreams" has illuminated the intricate relationship between ADHD and dream intensity. Key findings suggest that individuals with ADHD experience more vivid, emotionally charged, and frequent dreams, often reflecting their waking experiences and emotional state. This heightened dream intensity is linked to neurobiological differences, sleep disturbances, emotional dysregulation, cognitive difficulties, and co-occurring mental health conditions.
Understanding these connections has important implications for the treatment and management of ADHD. Addressing sleep hygiene, emotional regulation skills, and cognitive functioning can effectively reduce dream intensity and improve overall sleep quality. Furthermore, recognizing the long-term outcomes associated with intense dreams emphasizes the need for comprehensive interventions that support individuals with ADHD throughout their lives.
ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) What Is It?

ADHD & Conflict

Understanding The ADHD Brain